Introduction to Mediterranean Diet
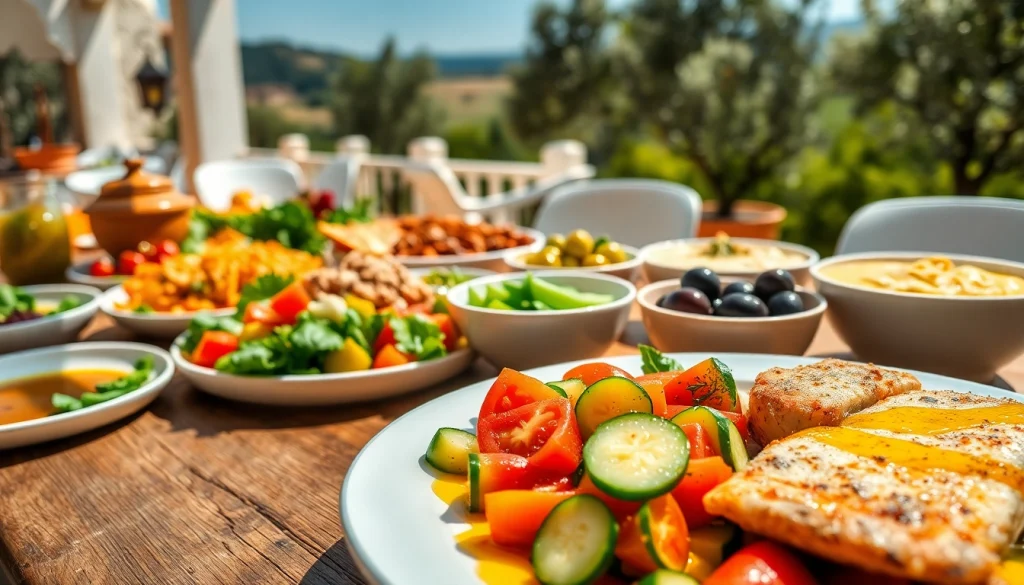
The Mediterranean diet has gained immense popularity worldwide, not only for its delicious flavors but also for its numerous health benefits. Characterized by a rich diversity of foods derived from traditional Mediterranean regions like Greece, Italy, and Spain, it promotes a lifestyle that favors plant-based eating while emphasizing healthy fats and lean proteins. By choosing the mediterranean diet, individuals can enhance their overall wellbeing and potentially mitigate the risk of chronic diseases.
What is the Mediterranean Diet?
At its core, the Mediterranean diet is more than just a nutritional plan—it’s a way of life that encompasses physical activity, social interactions, and a balanced approach to eating. This dietary pattern emphasizes whole foods—fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, fish, and moderate amounts of dairy and poultry—while greatly limiting processed foods, sugar, and red meats. The driving philosophy is to eat in moderation and to savor food, often featuring family meals that encourage sociability.
History and Origins of the Mediterranean Diet
The roots of the Mediterranean diet trace back to the historical agricultural practices, traditional culinary traditions, and eating habits of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. In the mid-20th century, Dr. Ancel Keys, an American epidemiologist, began studying the correlation between diet and health during his research in Italy and Greece. His findings paved the way for further understanding and acknowledgment of the diet as a model for healthy eating.
Key Components of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet comprises several key components, which work together to optimize health. These include:
- Vegetables and Fruits: Aiming for a variety of colors and types to maximize nutrient intake.
- Whole Grains: Including options like whole grain bread, brown rice, and quinoa.
- Healthy Fats: Primarily from olive oil and avocado, with moderate quantities of nuts and seeds.
- Lean Proteins: Predominantly from fish and poultry, with red meat consumed sparingly.
- Herbs and Spices: Using these instead of salt to enhance flavors naturally.
Health Benefits of Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is often lauded for its health benefits, with a wealth of research backing its positive effects on various aspects of health.
Cardiovascular Health and the Mediterranean Diet
One of the most significant benefits associated with the Mediterranean diet is its impact on heart health. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish), monounsaturated fats (primarily from olive oil), whole grains, and antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables has been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease. Studies indicate that adherence to this dietary pattern is linked to lower cholesterol levels, reduced blood pressure, and overall improved heart function.
Impact on Weight Management
The Mediterranean diet can also aid in weight management. Its focus on whole foods and nutrient-dense ingredients helps to curb hunger and promote satiety. Moreover, the diet’s balanced approach to fat and carbohydrates helps to stabilize blood sugar levels, reducing the likelihood of binge eating. Many individuals find that they are able to maintain a healthy weight without resorting to restrictive eating practices.
Long-Term Disease Prevention
Research has shown that the Mediterranean diet may play a significant role in the prevention of chronic diseases such as diabetes, certain types of cancer, and cognitive decline. The abundance of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods found in this diet can help mitigate oxidative stress and inflammation, which are underlying contributors to these conditions.
Foods to Include in Mediterranean Diet
Understanding the types of foods to include in the Mediterranean diet is crucial for reaping its benefits.
Fruits and Vegetables: The Core Staples
Fruits and vegetables are the pillars of the Mediterranean diet. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which contribute to overall health. Aim for a colorful plate by including a variety of seasonal produce. Leafy greens, tomatoes, cucumbers, citrus fruits, berries, and legumes should be incorporated daily to maximize nutritional intake.
Healthy Fats: Emphasizing Olive Oil
Extra virgin olive oil is the primary source of dietary fat in the Mediterranean diet, known for its heart-healthy benefits. It is packed with monounsaturated fats that help reduce bad cholesterol levels and provide anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporating olive oil through dressings, cooking, and dips is essential for maintaining a healthy balance of fats.
Lean Proteins and Whole Grains
Lean protein sources such as fish (especially fatty fish like salmon and sardines) and poultry are preferable. Red meat is consumed sparingly, often used as a flavoring rather than the main component of meals. Whole grains (like barley, farro, and whole wheat pasta) are favored over refined grains, enhancing fiber intake and vascular health.
Meal Planning for Mediterranean Diet
Effective meal planning is key to successfully adopting the Mediterranean diet and reaping its myriad benefits.
Creating a Weekly Meal Plan
To create a successful weekly meal plan, begin by outlining your meals for the week. Incorporate a variety of foods across the food groups. For instance, a typical day may include:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt topped with berries and nuts.
- Lunch: A salad with mixed greens, chickpeas, cherry tomatoes, olives, and a drizzle of olive oil.
- Dinner: Grilled fish with a side of quinoa and steamed vegetables.
- Snacks: Fresh fruit, mixed nuts, or hummus with vegetable sticks.
Planning meals ahead allows for balanced nutrition and reduces the temptation to resort to processed convenience foods.
Quick and Easy Mediterranean Recipes
With a plethora of simple recipes, incorporating the Mediterranean diet into daily life is achievable. Here are a few quick options:
- Chickpea Salad: Combine canned chickpeas, diced cucumber, bell pepper, red onion, parsley, olive oil, and lemon juice for a refreshing salad.
- Mediterranean Wrap: Use whole grain pita stuffed with grilled vegetables, feta cheese, and tzatziki sauce.
- Simple Pasta: Toss whole grain pasta with cherry tomatoes, spinach, garlic, and a sprinkle of feta for a quick meal.
Grocery Shopping Tips for Mediterranean Diet
When shopping for the Mediterranean diet, focus on the perimeter of the grocery store where fresh produce, meats, and dairy products are typically found. Look for seasonal and local options, and consider buying in bulk for grains and legumes. Always check labels to avoid added sugars and preservatives, ensuring that the foods you choose remain as close to their natural state as possible.
Overcoming Challenges with Mediterranean Diet
Adopting a new dietary pattern can be challenging. Overcoming common obstacles is essential for sustainable adherence to the Mediterranean diet.
Common Misconceptions about Mediterranean Diet
One common misconception is that the Mediterranean diet is overly restrictive or time-consuming. In reality, the diet is flexible and encourages a variety of foods. Meals can be simple and quick, and preparation can be minimized by batch cooking grains and legumes in advance. Additionally, many staple components, such as fruits and vegetables, can be enjoyed raw or cooked with minimal effort.
Adapting Mediterranean Diet to Different Lifestyles
The Mediterranean diet is adaptable to various lifestyles and dietary preferences. For those with plant-based preferences, the diet can focus on legumes, grains, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables. Omnivores can easily incorporate the recommended lean meats and dairy options, while gluten-free individuals can substitute traditional grains with quinoa, rice, or gluten-free pasta options. The essence of the Mediterranean diet is to enjoy food while making healthier choices.
Staying Motivated on Your Mediterranean Diet Journey
Long-term adherence to the Mediterranean diet may require some motivation. Set realistic goals and track your progress. Sharing meals with family and friends can enhance the experience and make the diet more enjoyable. Exploring new recipes and ingredients will keep meals exciting and inspire creativity in the kitchen. Lastly, understanding the dietary benefits and aligning them with personal health goals can further strengthen one’s commitment.